Tragedy of War Hero turned writer who lived in Epsom
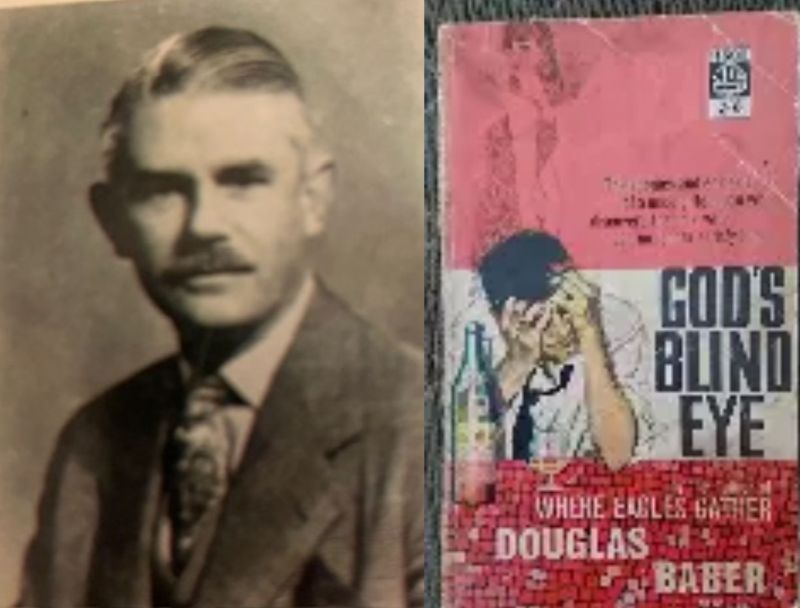
In June 1960, Douglas Baber, 42, was found comatose through drink in the garden of his former home in Woodcote Green, a well-to-do housing estate in Epsom. A court appearance followed, during which the magistrate noted that Baber had been before the Epsom bench seven times on drink-related charges. Baber, for his part, expressed appreciation for the care the Epsom constabulary had shown him while in custody. The Sutton and Epsom Advertiser described him as a “local author”, but there was far more to Douglas Gordon Baber than that.
Born in Belfast in 1918, he was living in middle-class comfort in South Croydon by 1921 in a household that included his mother Isabella, siblings and two servants. His father, Charles Johnstone Baber, was absent, later remarrying in 1929 and fathering a daughter, Hazel. Charles was an entrepreneur in the high-end footwear trade, at one time operating a shop on London’s Regent Street.
The family later moved to Bexhill on the south coast. At 11, Douglas came to public attention when newspapers reported his dramatic rescue after being swept out to sea by Channel currents — perhaps an early sign of the adventurous spirit that would define him. He developed a passion for flight and, in 1935 at just 17 years old, obtained a flying licence in a Gipsy Moth plane. On his certificate, he described himself as a student in boot and shoe manufacturing, likely intending to follow his father’s trade.
In 1937 Douglas travelled to Canada, finding work in factory administration. But the outbreak of the Second World War brought those plans to an end. He returned to England, enlisted in the RAF and, at 21, was flying bomber planes over occupied Europe as a Flight Lieutenant in 77 Squadron.
On 17 August 1941 he bailed out over Belgium and survived. He fled the crash site and was given refuge by the Rigaux family, farmers in Zingem, who risked their lives by sheltering him under German occupation. After nearly three weeks, German soldiers raided the farm following a suspected tip-off. Douglas was captured and the Rigaux family taken away to an uncertain fate. At Gestapo HQ in Brussels, he later said he was first subjected to rough treatment, then friendliness, then threats to shoot him — a deliberate psychological tactic.
Douglas passed through several POW camps: Dulag Luft in Germany, then Oflag XC in Lübeck, followed by Oflag VI-B Warburg, where he was imprisoned at the same time as the celebrated pilot Douglas Bader. The similarity in their names likely caused administrative confusion, and it is improbable the two men were not at least aware of each other.
In 1942 Baber was transferred to Oflag XXI-B Schubin in Poland, where fellow prisoners included future Chancellor Anthony Barber and Eric Williams, author of The Wooden Horse. He was later sent to Stalag Luft III at Sagan — now Zagan, Poland — famous for The Great Escape. Fellow prisoners included Paul Brickhill, who would later write Reach for the Sky, and actors Peter Butterworth and Rupert Davies. In February 1945 Douglas was moved again, to Marlag Nord, where he was soon liberated by Allied forces.
After returning home, Douglas collaborated with two former POWs to write Oflag 3, a play about prison camp life. Directed by Charles Hawtrey and featuring a young Pete Murray, it was staged at the X Theatre in Richmond and well received. Misleading online claims that Hawtrey collaborated with Douglas Bader rather than Douglas Baber have unfortunately muddied the historical record.
Douglas married Phyliss Fox in 1947. Their daughter Vivienne was born in 1950, and the family settled first in Christchurch Mount and later on the Woodcote Estate. His writing career flourished. He first signed with avant-garde publisher Werner Laurie, then with Heinemann, who released his debut crime novel My Death is a Mockery in 1952. The book, involving the murder of a policeman, was an immediate success and was quickly adapted into a film starring Donald Houston, Kathleen Byron and Bill Kerr.
The film became embroiled in the notorious Craig and Bentley case after Christopher Craig, the 16-year-old who shot PC Sidney Miles, revealed he had seen it earlier that day. Tabloid speculation unfairly pointed towards Baber, and he began receiving hate mail. This publicity placed immense strain on him and his family. Douglas had already shown vulnerability: in 1950 he was convicted of assaulting a ticket collector after a POW reunion. He expressed deep remorse in court, admitting to having drunk too much.
Through the 1950s Douglas published prolifically, producing Where Eagles Gather, The Guarded Years, Love on the Verge, A Road to Disaster, The Mortal Triumph and The Slender Thread, alongside short stories and journalism. He also published under the name John Ritson and worked as a publishing editor and executive. In 1956 he became advertising promotion manager at ABC TV, part of the early ITV network. On the surface, life in the stockbroker belt appeared successful.
But privately Douglas was spiralling. He increasingly found himself in Epsom Police Station for drink-related incidents, and once smashed his car into a shop in Bexhill. His marriage appears to have come under great strain. According to his daughter Vivienne, Douglas was devastated when he learned during the 1950s that members of the courageous Rigaux family who had sheltered him had been murdered by the Gestapo or deported to camps, where some later died. She said the guilt haunted him for the rest of his life.
It is easy to imagine how the emotional burden drove him towards alcohol. In 1963 he was still producing work — he published a short story in the Birmingham Evening Mail and took a post as advertisement controller on the Reverend Timothy Beaumont’s magazine Aspect. But on 21 October 1963 Douglas Gordon Baber died at 21 The Hill, Wheathampstead, near St Albans. He was only 45.
One of his later works, God’s Blind Eye (1960), features a businessman battling alcoholism. A line from the book seems to echo Baber’s own torment: “When the effects of the alcohol wore off, the sense of impending disaster and loneliness was far worse, crouched in his mind like an enemy.”