Epsom and Ewell Borough Council debt update
Councils across the UK have added a further £7.8bn to their collective borrowing in the last year, leaving local authorities with debts of £122.2bn – the equivalent of £1,791 for every resident. The figures, released by the Ministry of Housing, Communities and Local Government show that council debt rose seven per cent in a single year from £114.5bn in 2024.
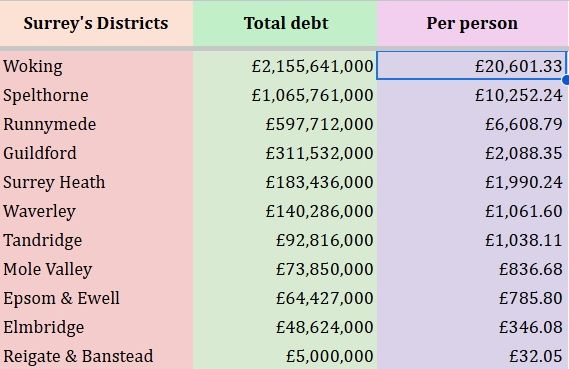
For Epsom and Ewell Borough Council (EEBC), debt at the end of the 2024/25 financial year stood at £64.4m – or £785.80 per head of population. Surrey County Council’s position is much larger in absolute terms, with borrowing of £1.07bn, equating to £873.69 per resident. EEBC’s debt level is exactly the same as the previous year. “This is because the council has not taken on any additional borrowing, and no debt was paid between the two financial years”, said Cllr Neil Dallen (RA Town Ward), Chair of EEBC’s Strategy and Resources Committee.
Both figures sit below the UK-wide average of £1,791 per head but illustrate how deeply embedded borrowing now is in local government finance.
Why councils borrow
Local authorities are permitted to borrow to fund projects such as schools, leisure centres, theatres and housing. Many also borrowed heavily over the past decade to acquire commercial property – from office parks to shopping centres – intended to generate rental income to offset cuts to central government funding.
But short-term borrowing from central government has almost tripled in recent years, in some cases used to plug day-to-day budget gaps rather than pay for long-term investments. Jonathan Carr-West of the Local Government Information Unit warned the approach was “extremely worrying”, likening it to “payday loans for local governments”.
Surrey’s position
Tim Oliver, Leader of Surrey County Council, said that while the council had “a stable budget position”, it was not immune to national financial pressures. He added: “All our key services – including social care, children’s services, and highways maintenance – are facing higher demand, higher costs, and reduced funding. We must find ways to continue to support those residents who need us most, and to deliver the services that people rely on every day.
“As part of our budget setting process, the levels of balances and reserves have been determined to ensure that the level is justifiable and manageable in the context of local circumstances and risk.”
Surrey’s capital spending ambitions include new school places, highways upgrades, green initiatives, social care accommodation and library improvements, but the council has been forced to hold more expensive short-term debt while waiting for interest rates to fall.
National concerns
Warnings about the sustainability of council borrowing are not new. Six authorities – Croydon, Slough, Thurrock, Birmingham, Woking and Nottingham – have effectively declared bankruptcy in recent years, in some cases due to failed investment schemes. Thurrock alone faces a £469m funding black hole from collapsed solar farm projects.
The Institute for Fiscal Studies has calculated that local authority “core spending power” remains 18% lower per resident than in 2010 despite some increases since the pandemic.
In June, Labour leader Sir Keir Starmer pledged an overhaul of the council grant system to simplify the funding formula and shift resources towards the most deprived areas. While welcomed by urban councils, rural authorities have raised concerns that redistribution could “overcompensate” and leave them exposed.
Cost of servicing debt
Separate analysis by the Times found that councils across Great Britain now spend the equivalent of a fifth of council tax revenues on servicing their debts. Annual interest costs are estimated at over £4bn – more than the combined national spend on emergency housing and libraries, culture and tourism.
The Local Government Association’s finance spokesperson, Cllr Pete Marland, said council finances “remain in a fragile position”, adding: “A sustainable, long-term financial model for local government must lead to all councils having adequate resources to meet growing cost and demand pressures.”
The local picture
Epsom and Ewell’s £64.4m debt may appear modest compared with Surrey County Council’s £1.07bn, but both authorities – like councils nationwide – must balance their budgets each year while contending with higher borrowing costs, reduced grant funding and rising demand for services.
With 30 more councils seeking exceptional financial support from government this year, including permission to use loans or asset sales to cover day-to-day spending, the pressure on local finances is set to remain intense.
The table below lists all of Surrey’s districts highest debt first for 2024/2025: